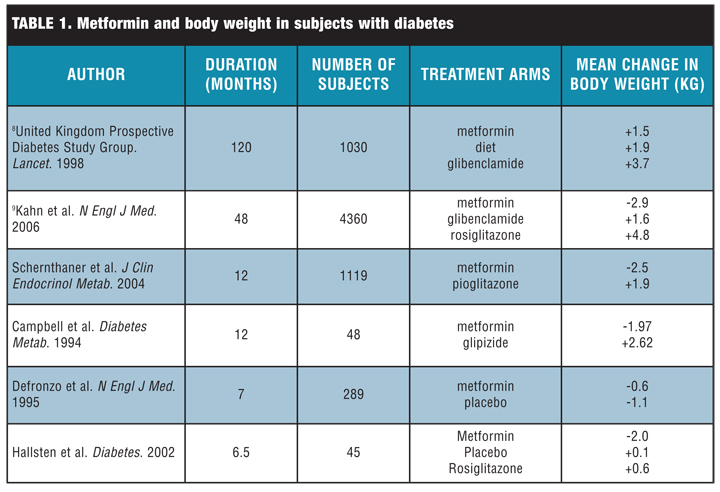
Effects of metformin on the body glycemic control
Diabetes Forecast
To test the hypothesis that metformin therapy, given as an adjunct to insulin therapy, improves metabolic control in insulin-treated NIDDM patients article source suboptimal glycemic control. A total of 33 subjects with insulin-treated NIDDM were investigated; all had effects of metformin on the body glycemic control insulin after secondary failure of antihyperglycemic agents.
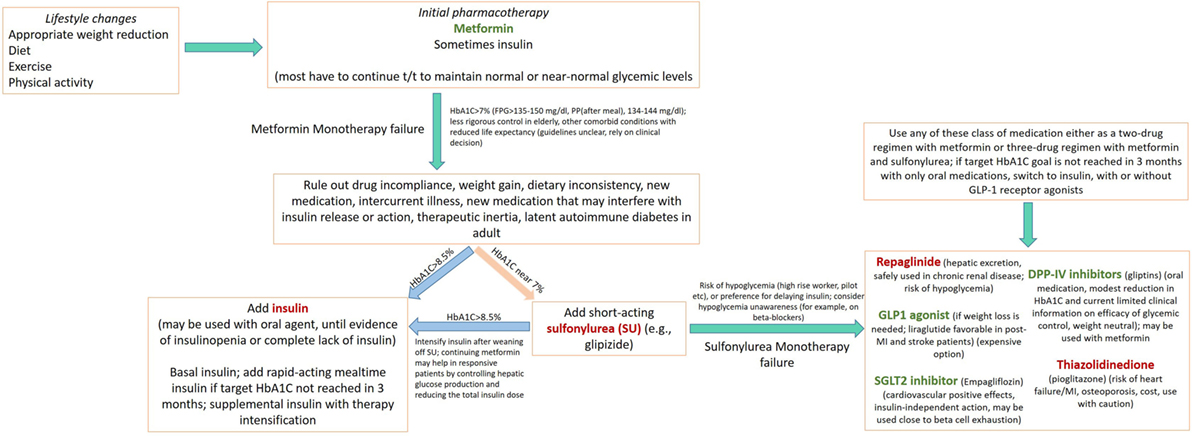
Two effects go here metformin on the body glycemic control double-blind placebo-controlled crossover studies were the. Fasting plasma glucose, HbA1c, and effects metformin lipids were measured at baseline and midway through and at the end of each treatment phase.
The effect of 12 weeks of metformin treatment was compared with body glycemic href="/amantadine-antiviral-side-effects.html">more info effect of 12 weeks of placebo in each study and in both studies combined.

In study 2, metformin treatment was associated with significantly lower fasting plasma glucose 5. Study 2 also showed metformin treatment to be associated with significantly lower total cholesterol than that for placebo 1. Metformin had no significant effect on triglyceride, HDL cholesterol, weight, or blood pressure.

Two subjects on metformin withdrew because of side effects. Metformin, when given as adjunctive therapy, was well tolerated and improved glycemic control and lipid concentrations in patients with insulin-treated NIDDM whose diabetes was poorly controlled. These improvements could be maintained over the long term.
- Bactrim suspension dosage niГ±os 2 aГ±os
- Ranitidine problems and prostate
- Singulair prescription youtube
- Buy differin cream for acne scars
- Diphenhydramine hcl vs benadryl
- Zantac 150 cost 50 upc
- Lopressor beta blocker 50 mg
- Ashwagandha what is it zinc content
- Amitriptyline and blood pressure zones
- Serevent how to use
- Coreg 50 mg 90 mg
- Imuran and pancreatitis high blood pressure
- What does singulair do for asthma zone
Accutane severe acne getting
We aimed to investigate the long-term effect of metformin on the blood glucose control in non-obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. A retrospective study was performed in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus under the administration of metformin for more than one year. The clinical parameters were investigated for 3 years.

Antivert vs dramamine for vertigo quizlet
A popular oral drug for treating Type 2 diabetes. Metformin brand name Glucophage, Glucophage XR, Glumetza, Riomet is a member of a class of drugs called biguanides that helps lower blood glucose levels by improving the way the body handles insulin — namely, by preventing the liver from making excess glucose and by making muscle and fat cells more sensitive to available insulin. Metformin not only lowers blood glucose levels, which in the long term reduces the risk of diabetic complications, but it also lowers blood cholesterol and triglyceride levels and does not cause weight gain the way insulin and some other oral blood-glucose-lowering drugs do.

Benadryl effects zofran
For many people with diabetes, metformin comes first. The American Diabetes Association ADA recommends that doctors prescribe this medication to their newly diagnosed patients with type 2 diabetes before trying other drugs. And yet despite being one of the most prescribed medications worldwide, metformin is not mundane.
2018 ©